„Experiments with microwaves” változatai közötti eltérés
A Fizipedia wikiből
| 1. sor: | 1. sor: | ||
| + | <wlatex> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
''Aim of the experiment'' | ''Aim of the experiment'' | ||
*To deepen the knowledge related to wave phenomena, | *To deepen the knowledge related to wave phenomena, | ||
| 12. sor: | 15. sor: | ||
==Theoretical summary== | ==Theoretical summary== | ||
| − | + | ||
In the experiment we use microwaves to study wave phenomena. Microwaves - as well as light - are electromagnetic waves of wavelength about 1 mm - 30 cm (correspondingly, the frequency of microwaves is $ 10^{9} - 3 \cdot 10^{11}\ \text{Hz} $). | In the experiment we use microwaves to study wave phenomena. Microwaves - as well as light - are electromagnetic waves of wavelength about 1 mm - 30 cm (correspondingly, the frequency of microwaves is $ 10^{9} - 3 \cdot 10^{11}\ \text{Hz} $). | ||
A lap 2018. július 3., 12:28-kori változata
Aim of the experiment
- To deepen the knowledge related to wave phenomena,
- To verify the relationships in wave physics experimentally,
- To model phenomena and devices in wave optics.
For the purpose:
- We summarize the basic knowledge on wave phenomena,
- We examine reflection, refraction, interference and diffraction of microwaves,
- We assemble some experimental setups (which are also useful in optics) based on interference of waves, and measure the wavelength of the used microwave.
Tartalomjegyzék[elrejtés] |
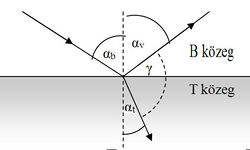
Theoretical summary
In the experiment we use microwaves to study wave phenomena. Microwaves - as well as light - are electromagnetic waves of wavelength about 1 mm - 30 cm (correspondingly, the frequency of microwaves is 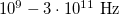 ).
).
Polarization of waves
In a transversal wave the vector related to the changing quantity is in the plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation but within this plane its direction is arbitrary.