„Thermoelectric phenomena” változatai közötti eltérés
(Új oldal, tartalma: „__TOC__ <wlatex> A Landauer-formula tárgyalásakor láttuk, hogy egy elektródából …”) |
|||
| 1. sor: | 1. sor: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
<wlatex> | <wlatex> | ||
| − | + | Dealing with the [[Electron transport in nanowires: Landauer formula, conductance quantization|Landauer formula]], we learned that the current flowing from one electrode into the single-channel nanowire is derived from the integration of the Fermi function of the given electrode with respect to the energy: | |
| + | |||
$$\frac{2}{L} \sum (-e) \cdot v_k \cdot f(\varepsilon_k) = -\frac{2}{h}\int e\cdot f(\varepsilon)\,\mathrm{d} \varepsilon \rightarrow I.$$ | $$\frac{2}{L} \sum (-e) \cdot v_k \cdot f(\varepsilon_k) = -\frac{2}{h}\int e\cdot f(\varepsilon)\,\mathrm{d} \varepsilon \rightarrow I.$$ | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | $$I=\frac{2 e}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T}\cdot [f_1(\varepsilon)-f_2(\varepsilon)]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon$$ | + | If we apply $V$ bias across the electrodes of a single-channel nanowire containing a scattering centre with transmission probability $\mathcal{T}$, the current flowing through the nanowire is |
| + | $$I=\frac{2 e}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T}\cdot [f_1(\varepsilon)-f_2(\varepsilon)]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon,$$ | ||
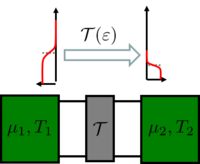
| + | therefore, the conductance is $G=(2e^2/h)\cdot\mathcal{T}$. In the following, we examine what happens if not only the chemical potentials of the electrodes differ but they are also at different temperatures (figure 1.). | ||
| + | |||
{| cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" align="center" | {| cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" align="center" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center"|[[Fájl:Termoelectric1.png|közép|200px]] | | align="center"|[[Fájl:Termoelectric1.png|közép|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | align="center"|1 | + | | align="center"|Figure 1. ''We are interested in the thermal conduction properties of a single-channel nanowire with a scattering centre with transmission probability $\mathcal{T}$ between two electrodes with different chemical potentials and at different temperatures.'' |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | The electric current is calculated with the same equation above, but we need to take into account that the Fermi functions differ not only in the chemical potential but also in the temperature: | |
$$I=\frac{2 e}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot \left[f_1(\varepsilon,\mu_1,T_1)-f_2(\varepsilon,\mu_2,T_2)\right]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon.$$ | $$I=\frac{2 e}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot \left[f_1(\varepsilon,\mu_1,T_1)-f_2(\varepsilon,\mu_2,T_2)\right]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon.$$ | ||
| − | + | Similarly to the relation $dQ=dE-\mu dN$ known from thermodynamics, we can derive thermal current $I_Q$ flowing from one electrode into the nanowire: | |
$$\frac{2}{L} \sum (\varepsilon_k-\mu) \cdot v_k \cdot f(\varepsilon_k) = \frac{2}{h}\int (\varepsilon-\mu) \cdot f(\varepsilon)\,\mathrm{d} \varepsilon \rightarrow I_Q,$$ | $$\frac{2}{L} \sum (\varepsilon_k-\mu) \cdot v_k \cdot f(\varepsilon_k) = \frac{2}{h}\int (\varepsilon-\mu) \cdot f(\varepsilon)\,\mathrm{d} \varepsilon \rightarrow I_Q,$$ | ||
| − | + | therefore, the thermal current flowing from one electrode to the other given a transmission probability $\mathcal{T}$: | |
$$I_Q=\frac{2}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot (\varepsilon-\mu_1)\cdot \left[f_1(\varepsilon,\mu_1,T_1)-f_2(\varepsilon,\mu_2,T_2)\right]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon.$$ | $$I_Q=\frac{2}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot (\varepsilon-\mu_1)\cdot \left[f_1(\varepsilon,\mu_1,T_1)-f_2(\varepsilon,\mu_2,T_2)\right]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon.$$ | ||
| − | + | It is important to note here that in the equation above $(\varepsilon-\mu_1)$ is the multiplication factor because we calculated the thermal current flowing from/to electrode 1. If we were to calculate the thermal current flowing from/to electrode 2, we would have to change the multiplication factor to $(\varepsilon-\mu_2)$. As the two calculations have to give the same thermal current, the two calculations certainly lead to the same result. | |
| − | + | Based on this, in addition to the calculation of the electric conductance (Landauer formula) we can also determine the heat conductance, as well as the Seebeck and Peltier coefficients of the system. | |
</wlatex> | </wlatex> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Seebeck effect== |
<wlatex> | <wlatex> | ||
| − | + | Let us calculate the electric current flowing through the system depicted in figure 1. if the temperatures of the two electrodes are different! For this, we apply the Sommerfeld expansion learned in the [[a szilárdtestfizika alapjai|Basics of solid-state physics]] course, which approximates the integral of the multiplication of an arbitrary energy dependent function and the Fermi function: | |
$$\int_{-\infty}^\infty H(\varepsilon)\cdot f(\varepsilon,\mu,T)\,\mathrm{d}\varepsilon = \int_{-\infty}^\mu H(\varepsilon)\,\mathrm{d}\varepsilon + \frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT)^2 H^\prime(\mu) + \mathrm{O} \left(\frac{kT}{\mu}\right)^4.$$ | $$\int_{-\infty}^\infty H(\varepsilon)\cdot f(\varepsilon,\mu,T)\,\mathrm{d}\varepsilon = \int_{-\infty}^\mu H(\varepsilon)\,\mathrm{d}\varepsilon + \frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT)^2 H^\prime(\mu) + \mathrm{O} \left(\frac{kT}{\mu}\right)^4.$$ | ||
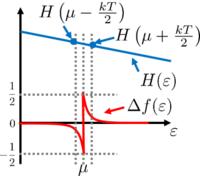
| − | + | The Sommerfeld expansion relies on the approximation of the Fermi function as $f(\varepsilon,\mu,T) \approx f(\varepsilon,\mu,T=0)+\Delta f$ where $\Delta f=f(\varepsilon,\mu,T)-f(\varepsilon,\mu,T=0)$ is illustrated in figure 2. The first term of the Sommerfeld expansion is the integration with the Fermi function evaluated at zero temperature which is a stepfunction that becomes zero at $\varepsilon=\mu$. The second term $(\int H(\varepsilon)\Delta f)$ in case of an energy independent $H$ logically gives zero (see figure 2.), therefore the integral is proportional to $H'(\mu)$. According to figure 2 even the $(kT)^2$ dependence is understandable. | |
{| cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" align="center" | {| cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" align="center" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center"|[[Fájl:Termoelektromos2.png|közép|200px]] | | align="center"|[[Fájl:Termoelektromos2.png|közép|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | align="center"|2 | + | | align="center"|Figure 2. ''Illustration of the Sommerfeld expansion. The (equal) areas below the positive and negative peaks seen in function $\Delta f$ are on the order of $kT$, so $\int H(\varepsilon)\Delta f\mathrm{d}\varepsilon \sim kT\cdot H(\mu+kT/2) - kT\cdot H(\mu-kT/2)\approx (kT)^2\cdot H'(\mu)$.'' |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | According to the Sommerfeld expansion: | |
$$I=\frac{2 e}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot \left[f_1(\varepsilon,\mu_1,T_1)-f_2(\varepsilon,\mu_2,T_2)\right]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon\approx\frac{2 e}{h} \cdot \int_{\mu_2}^{\mu_1} \mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)\,\mathrm{d}\varepsilon +\frac{2 e}{h}\frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT_1)^2 \mathcal{T}^\prime(\mu_1)-\frac{2 e}{h}\frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT_2)^2 \mathcal{T}^\prime(\mu_2).$$ | $$I=\frac{2 e}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot \left[f_1(\varepsilon,\mu_1,T_1)-f_2(\varepsilon,\mu_2,T_2)\right]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon\approx\frac{2 e}{h} \cdot \int_{\mu_2}^{\mu_1} \mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)\,\mathrm{d}\varepsilon +\frac{2 e}{h}\frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT_1)^2 \mathcal{T}^\prime(\mu_1)-\frac{2 e}{h}\frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT_2)^2 \mathcal{T}^\prime(\mu_2).$$ | ||
| − | + | If we only consider linear energy-dependence of $\mathcal{T}$, then $\mathcal{T}^\prime(\mu_2)=\mathcal{T}^\prime(\mu_1)$ and: | |
$$I\approx \frac{2 e}{h} \cdot eV \cdot\bar{\mathcal{T}}(\varepsilon)+\frac{2 e}{h}\frac{\pi^2 k^2}{3}\cdot\Delta T\cdot T \cdot\mathcal{T}^\prime(\mu),$$ | $$I\approx \frac{2 e}{h} \cdot eV \cdot\bar{\mathcal{T}}(\varepsilon)+\frac{2 e}{h}\frac{\pi^2 k^2}{3}\cdot\Delta T\cdot T \cdot\mathcal{T}^\prime(\mu),$$ | ||
| − | + | where $\Delta T=T_1-T_2$, $\ \ T=(T_1+T_2)/2$, $\ \ \mu=(\mu_1+\mu_2)/2$, and $\bar{\mathcal{T}}$ is the average transmission probability in the range between $\mu_1$ and $\mu_2$. Suppose that we connect a voltmeter with an internal resistance of infinity between the two electrodes. Consequently, the current flowing through the nanowire is zero. If the temperatures of the electrodes are equal, the equation above is simplified to the Landauer formula which implies that at zero current zero voltage is measured. On the other hand, if the temperature of the electrodes differ then for zero current | |
$$V \big|_{I=0}=\underbrace{-\frac{\pi^2 k^2 T}{3e}\cdot \frac{1}{\mathcal{T}}\frac{\partial \mathcal{T}(\varepsilon )}{\partial \varepsilon} \bigg|_{\mu}}_{S} \cdot \Delta T$$ | $$V \big|_{I=0}=\underbrace{-\frac{\pi^2 k^2 T}{3e}\cdot \frac{1}{\mathcal{T}}\frac{\partial \mathcal{T}(\varepsilon )}{\partial \varepsilon} \bigg|_{\mu}}_{S} \cdot \Delta T$$ | ||
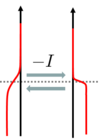
| − | + | voltage appears, where $S$ is the Seebeck coefficient of the nanowire. It is clear from this expression that large voltages are measured for strongly energy-dependent transmission. To understand this phenomenon let us look at figure 3! First, suppose that the chemical potentials of the electrodes are equal. This means that on the warmer side there are more occupied states above the common chemical potential, thus electrons start to go towards the colder side. However, below the common chemical potential more occupied states are to be found on the colder side, i.e. the electrons start to go in the direction of the warmer electrode. If the transmission is energy independent, the opposite sign current components above and below the common chemical potential are equal, so there is no charge transport. However, if the transmission strongly depends on the energy, the two current components differ significantly, which activates a charge transport between the two sides. The charge transport leads to a finite voltage between the two electrodes in which the current flowing through the nanowire becomes zero. | |
| + | |||
{| cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" align="center" | {| cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" align="center" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center"|[[Fájl:Termoelektromos3.png|közép|100px]] | | align="center"|[[Fájl:Termoelektromos3.png|közép|100px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | align="center"|3 | + | | align="center"|Figure 3. ''Illustration of the physical background of the Seebeck effect.'' |
|} | |} | ||
</wlatex> | </wlatex> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Heat conductance, Wiedemann-Franz law== |
<wlatex> | <wlatex> | ||
| − | + | As the next step, let us calculate the thermal current between two electrodes for zero potential-difference ($\mu_1=\mu_2=\mu$) and finite temperature-difference $T_1\neq T_2$ esetén. One can easily apply the Sommerfeld expansion on the equation for the thermal current, as the zeroth order term cancels due to the equal chemical potentials: | |
$$I_Q=\frac{2}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot (\varepsilon-\mu)\cdot \left[f_1(\varepsilon,\mu,T_1)-f_2(\varepsilon,\mu,T_2)\right]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon\approx\frac{2}{h}\frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT_1)^2\cdot\left[\mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot (\varepsilon-\mu)\right]'_\mu -\frac{2}{h}\frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT_2)^2\cdot \left[\mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot (\varepsilon-\mu)\right]'_\mu =\frac{2}{h}\frac{\pi^2 k^2}{3}\cdot\Delta T\cdot T \cdot \mathcal{T}(\mu).$$ | $$I_Q=\frac{2}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot (\varepsilon-\mu)\cdot \left[f_1(\varepsilon,\mu,T_1)-f_2(\varepsilon,\mu,T_2)\right]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon\approx\frac{2}{h}\frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT_1)^2\cdot\left[\mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot (\varepsilon-\mu)\right]'_\mu -\frac{2}{h}\frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT_2)^2\cdot \left[\mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot (\varepsilon-\mu)\right]'_\mu =\frac{2}{h}\frac{\pi^2 k^2}{3}\cdot\Delta T\cdot T \cdot \mathcal{T}(\mu).$$ | ||
| − | + | We can define the thermal conductance as: $$G_Q=I_Q/ \Delta T$$ | |
| − | + | which leads to: | |
| − | $$G_Q=\frac{2}{h}\frac{\pi^2 k^2}{3}\cdot T \cdot \mathcal{T}(\mu)$$ | + | $$G_Q=\frac{2}{h}\frac{\pi^2 k^2}{3}\cdot T \cdot \mathcal{T}(\mu).$$ |
| − | + | Comparing this to the electrical conductance $G=(2e^2/h)\cdot\mathcal{T}$ obtained from the Landauer formula: | |
$$\frac{G_Q}{G}=\mathcal{L}\cdot T;\ \ \ \mathcal{L}=\frac{\pi^2k^2}{3e^2}=2.44\times 10^{-8}\,\mathrm{W\,\Omega\,K^{-2}}$$, | $$\frac{G_Q}{G}=\mathcal{L}\cdot T;\ \ \ \mathcal{L}=\frac{\pi^2k^2}{3e^2}=2.44\times 10^{-8}\,\mathrm{W\,\Omega\,K^{-2}}$$, | ||
| − | + | where $\mathcal{L}$ is the so-called Lorenz number. This relation shows that the electrical conductance is proportional to the thermal conductance, which is referred to as the Wiedemann-Franz law. However, it is important to note that thermal conduction may be caused by phonons, which we did not take into account in our calculations. | |
</wlatex> | </wlatex> | ||
| − | ==Peltier | + | ==Peltier effect== |
<wlatex> | <wlatex> | ||
| − | + | Finally, let us examine the process opposite to the Seebeck effect which is called the Peltier effect. In this process at zero temperature-difference ($T_1=T_2=T$), a finite thermal current starts to flow due to an electric current flowing through the nanowire. It is important to emphasise that the temperature-difference is zero because if it was finite, beside the thermal current from the Peltier effect another thermal current contribution would arise due to heat conduction. One can calculate the thermal current utilizing again the Sommerfeld expansion: | |
$$I_Q=\frac{2}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot (\varepsilon-\mu_1)\cdot \left[f_1(\varepsilon,\mu_1,T)-f_2(\varepsilon,\mu_2,T)\right]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon\approx\frac{2}{h} \cdot \underbrace{\int_{\mu_2}^{\mu_1} \mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)(\varepsilon-\mu_1)\,\mathrm{d}\varepsilon}_{\sim (eV)^2} +\frac{2}{h}\frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT)^2\left[\overbrace{\underbrace{\left(\mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)(\varepsilon-\mu_1)\right)^\prime |_{\mu_1}}_{\mathcal{T}(\mu_1)}- \underbrace{\left(\mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)(\varepsilon-\mu_1)\right)^\prime|_{\mu_2}}_{\mathcal{T}^\prime (\mu_2)(\mu_2-\mu_1)+\mathcal{T}(\mu_2)}}^{2\mathcal{T}^\prime (\mu)\cdot eV}\right].$$ | $$I_Q=\frac{2}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot (\varepsilon-\mu_1)\cdot \left[f_1(\varepsilon,\mu_1,T)-f_2(\varepsilon,\mu_2,T)\right]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon\approx\frac{2}{h} \cdot \underbrace{\int_{\mu_2}^{\mu_1} \mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)(\varepsilon-\mu_1)\,\mathrm{d}\varepsilon}_{\sim (eV)^2} +\frac{2}{h}\frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT)^2\left[\overbrace{\underbrace{\left(\mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)(\varepsilon-\mu_1)\right)^\prime |_{\mu_1}}_{\mathcal{T}(\mu_1)}- \underbrace{\left(\mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)(\varepsilon-\mu_1)\right)^\prime|_{\mu_2}}_{\mathcal{T}^\prime (\mu_2)(\mu_2-\mu_1)+\mathcal{T}(\mu_2)}}^{2\mathcal{T}^\prime (\mu)\cdot eV}\right].$$ | ||
| − | + | The first term in the Sommerfeld expansion gives a second-order contribution in the voltage, thus one can neglect it. If we reorder the remaining terms, the result for the thermal current: | |
| − | $$I_Q\approx \frac{2e}{h}\frac{\pi^2 k^2 T^2}{3}\cdot \frac{\partial \mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)}{\partial \varepsilon}\bigg|_\mu \cdot V$$ | + | $$I_Q\approx \frac{2e}{h}\frac{\pi^2 k^2 T^2}{3}\cdot \frac{\partial \mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)}{\partial \varepsilon}\bigg|_\mu \cdot V.$$ |
| − | + | The Peltier coefficient is defined as the ratio of the thermal current and the electric current $I= -(2e^2/h)\cdot\mathcal{T}\cdot V$: | |
$$\frac{I_Q}{I}\bigg|_{T_1=T_2}\approx -\frac{\pi^2 k^2 T^2}{3e}\cdot \frac{1}{\mathcal{T}}\frac{\partial \mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)}{\partial \varepsilon}\bigg|_\mu =\Pi=T\cdot S.$$ | $$\frac{I_Q}{I}\bigg|_{T_1=T_2}\approx -\frac{\pi^2 k^2 T^2}{3e}\cdot \frac{1}{\mathcal{T}}\frac{\partial \mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)}{\partial \varepsilon}\bigg|_\mu =\Pi=T\cdot S.$$ | ||
| − | + | Comparing this result with the Seebeck coefficient we get: $\Pi=T\cdot S$ which is referred to as the Kelvin relation. | |
</wlatex> | </wlatex> | ||
A lap jelenlegi, 2019. május 17., 18:20-kori változata
Tartalomjegyzék |
Dealing with the Landauer formula, we learned that the current flowing from one electrode into the single-channel nanowire is derived from the integration of the Fermi function of the given electrode with respect to the energy:
![\[\frac{2}{L} \sum (-e) \cdot v_k \cdot f(\varepsilon_k) = -\frac{2}{h}\int e\cdot f(\varepsilon)\,\mathrm{d} \varepsilon \rightarrow I.\]](/images/math/0/1/f/01ff36396dc5d21d21e83053358e9837.png)
If we apply 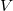 bias across the electrodes of a single-channel nanowire containing a scattering centre with transmission probability
bias across the electrodes of a single-channel nanowire containing a scattering centre with transmission probability 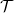 , the current flowing through the nanowire is
, the current flowing through the nanowire is
![\[I=\frac{2 e}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T}\cdot [f_1(\varepsilon)-f_2(\varepsilon)]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon,\]](/images/math/1/4/b/14b5f5545447a78cf6eff6d0f9b881b8.png)
therefore, the conductance is 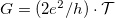 . In the following, we examine what happens if not only the chemical potentials of the electrodes differ but they are also at different temperatures (figure 1.).
. In the following, we examine what happens if not only the chemical potentials of the electrodes differ but they are also at different temperatures (figure 1.).
Figure 1. We are interested in the thermal conduction properties of a single-channel nanowire with a scattering centre with transmission probability 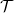 between two electrodes with different chemical potentials and at different temperatures. between two electrodes with different chemical potentials and at different temperatures.
|
The electric current is calculated with the same equation above, but we need to take into account that the Fermi functions differ not only in the chemical potential but also in the temperature:
![\[I=\frac{2 e}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot \left[f_1(\varepsilon,\mu_1,T_1)-f_2(\varepsilon,\mu_2,T_2)\right]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon.\]](/images/math/1/1/a/11a7d30cf8ace5ca12ec3b660bc01091.png)
Similarly to the relation 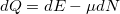 known from thermodynamics, we can derive thermal current
known from thermodynamics, we can derive thermal current 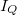 flowing from one electrode into the nanowire:
flowing from one electrode into the nanowire:
![\[\frac{2}{L} \sum (\varepsilon_k-\mu) \cdot v_k \cdot f(\varepsilon_k) = \frac{2}{h}\int (\varepsilon-\mu) \cdot f(\varepsilon)\,\mathrm{d} \varepsilon \rightarrow I_Q,\]](/images/math/e/5/e/e5e2f1b89306ae0af61710e422983a02.png)
therefore, the thermal current flowing from one electrode to the other given a transmission probability 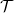 :
:
![\[I_Q=\frac{2}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot (\varepsilon-\mu_1)\cdot \left[f_1(\varepsilon,\mu_1,T_1)-f_2(\varepsilon,\mu_2,T_2)\right]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon.\]](/images/math/9/1/7/917f989f7ef7cf7ead4bbd7f1db12036.png)
It is important to note here that in the equation above 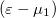 is the multiplication factor because we calculated the thermal current flowing from/to electrode 1. If we were to calculate the thermal current flowing from/to electrode 2, we would have to change the multiplication factor to
is the multiplication factor because we calculated the thermal current flowing from/to electrode 1. If we were to calculate the thermal current flowing from/to electrode 2, we would have to change the multiplication factor to 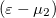 . As the two calculations have to give the same thermal current, the two calculations certainly lead to the same result.
. As the two calculations have to give the same thermal current, the two calculations certainly lead to the same result.
Based on this, in addition to the calculation of the electric conductance (Landauer formula) we can also determine the heat conductance, as well as the Seebeck and Peltier coefficients of the system.
Seebeck effect
Let us calculate the electric current flowing through the system depicted in figure 1. if the temperatures of the two electrodes are different! For this, we apply the Sommerfeld expansion learned in the Basics of solid-state physics course, which approximates the integral of the multiplication of an arbitrary energy dependent function and the Fermi function:
![\[\int_{-\infty}^\infty H(\varepsilon)\cdot f(\varepsilon,\mu,T)\,\mathrm{d}\varepsilon = \int_{-\infty}^\mu H(\varepsilon)\,\mathrm{d}\varepsilon + \frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT)^2 H^\prime(\mu) + \mathrm{O} \left(\frac{kT}{\mu}\right)^4.\]](/images/math/b/9/c/b9c065d10d8f8bd34d2112173f294c8e.png)
The Sommerfeld expansion relies on the approximation of the Fermi function as 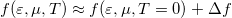 where
where 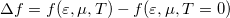 is illustrated in figure 2. The first term of the Sommerfeld expansion is the integration with the Fermi function evaluated at zero temperature which is a stepfunction that becomes zero at
is illustrated in figure 2. The first term of the Sommerfeld expansion is the integration with the Fermi function evaluated at zero temperature which is a stepfunction that becomes zero at 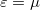 . The second term
. The second term 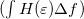 in case of an energy independent
in case of an energy independent 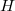 logically gives zero (see figure 2.), therefore the integral is proportional to
logically gives zero (see figure 2.), therefore the integral is proportional to 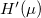 . According to figure 2 even the
. According to figure 2 even the 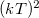 dependence is understandable.
dependence is understandable.
Figure 2. Illustration of the Sommerfeld expansion. The (equal) areas below the positive and negative peaks seen in function 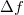 are on the order of are on the order of 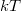 , so , so 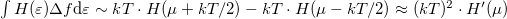 . .
|
According to the Sommerfeld expansion:
![\[I=\frac{2 e}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot \left[f_1(\varepsilon,\mu_1,T_1)-f_2(\varepsilon,\mu_2,T_2)\right]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon\approx\frac{2 e}{h} \cdot \int_{\mu_2}^{\mu_1} \mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)\,\mathrm{d}\varepsilon +\frac{2 e}{h}\frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT_1)^2 \mathcal{T}^\prime(\mu_1)-\frac{2 e}{h}\frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT_2)^2 \mathcal{T}^\prime(\mu_2).\]](/images/math/4/e/9/4e9ae7dfcf026a29b446e1529bd983c4.png)
If we only consider linear energy-dependence of 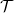 , then
, then 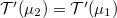 and:
and:
![\[I\approx \frac{2 e}{h} \cdot eV \cdot\bar{\mathcal{T}}(\varepsilon)+\frac{2 e}{h}\frac{\pi^2 k^2}{3}\cdot\Delta T\cdot T \cdot\mathcal{T}^\prime(\mu),\]](/images/math/1/f/d/1fd3b23c04a789032940f9e00ea03fa8.png)
where 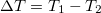 ,
, 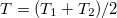 ,
, 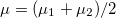 , and
, and 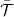 is the average transmission probability in the range between
is the average transmission probability in the range between 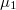 and
and 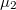 . Suppose that we connect a voltmeter with an internal resistance of infinity between the two electrodes. Consequently, the current flowing through the nanowire is zero. If the temperatures of the electrodes are equal, the equation above is simplified to the Landauer formula which implies that at zero current zero voltage is measured. On the other hand, if the temperature of the electrodes differ then for zero current
. Suppose that we connect a voltmeter with an internal resistance of infinity between the two electrodes. Consequently, the current flowing through the nanowire is zero. If the temperatures of the electrodes are equal, the equation above is simplified to the Landauer formula which implies that at zero current zero voltage is measured. On the other hand, if the temperature of the electrodes differ then for zero current
![\[V \big|_{I=0}=\underbrace{-\frac{\pi^2 k^2 T}{3e}\cdot \frac{1}{\mathcal{T}}\frac{\partial \mathcal{T}(\varepsilon )}{\partial \varepsilon} \bigg|_{\mu}}_{S} \cdot \Delta T\]](/images/math/1/f/d/1fd92f9d3dbf2d94361fcda8c71cbd4b.png)
voltage appears, where 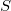 is the Seebeck coefficient of the nanowire. It is clear from this expression that large voltages are measured for strongly energy-dependent transmission. To understand this phenomenon let us look at figure 3! First, suppose that the chemical potentials of the electrodes are equal. This means that on the warmer side there are more occupied states above the common chemical potential, thus electrons start to go towards the colder side. However, below the common chemical potential more occupied states are to be found on the colder side, i.e. the electrons start to go in the direction of the warmer electrode. If the transmission is energy independent, the opposite sign current components above and below the common chemical potential are equal, so there is no charge transport. However, if the transmission strongly depends on the energy, the two current components differ significantly, which activates a charge transport between the two sides. The charge transport leads to a finite voltage between the two electrodes in which the current flowing through the nanowire becomes zero.
is the Seebeck coefficient of the nanowire. It is clear from this expression that large voltages are measured for strongly energy-dependent transmission. To understand this phenomenon let us look at figure 3! First, suppose that the chemical potentials of the electrodes are equal. This means that on the warmer side there are more occupied states above the common chemical potential, thus electrons start to go towards the colder side. However, below the common chemical potential more occupied states are to be found on the colder side, i.e. the electrons start to go in the direction of the warmer electrode. If the transmission is energy independent, the opposite sign current components above and below the common chemical potential are equal, so there is no charge transport. However, if the transmission strongly depends on the energy, the two current components differ significantly, which activates a charge transport between the two sides. The charge transport leads to a finite voltage between the two electrodes in which the current flowing through the nanowire becomes zero.
| Figure 3. Illustration of the physical background of the Seebeck effect. |
Heat conductance, Wiedemann-Franz law
As the next step, let us calculate the thermal current between two electrodes for zero potential-difference (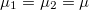 ) and finite temperature-difference
) and finite temperature-difference 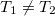 esetén. One can easily apply the Sommerfeld expansion on the equation for the thermal current, as the zeroth order term cancels due to the equal chemical potentials:
esetén. One can easily apply the Sommerfeld expansion on the equation for the thermal current, as the zeroth order term cancels due to the equal chemical potentials:
![\[I_Q=\frac{2}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot (\varepsilon-\mu)\cdot \left[f_1(\varepsilon,\mu,T_1)-f_2(\varepsilon,\mu,T_2)\right]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon\approx\frac{2}{h}\frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT_1)^2\cdot\left[\mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot (\varepsilon-\mu)\right]'_\mu -\frac{2}{h}\frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT_2)^2\cdot \left[\mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot (\varepsilon-\mu)\right]'_\mu =\frac{2}{h}\frac{\pi^2 k^2}{3}\cdot\Delta T\cdot T \cdot \mathcal{T}(\mu).\]](/images/math/3/a/9/3a98f2d375a7a1d85c238a5eac177d1d.png)
![\[G_Q=I_Q/ \Delta T\]](/images/math/7/0/5/7056b7f9b49a7eaf191393339894d6aa.png)
which leads to:
![\[G_Q=\frac{2}{h}\frac{\pi^2 k^2}{3}\cdot T \cdot \mathcal{T}(\mu).\]](/images/math/d/0/4/d04d1b5e5e364c54cb2125339cf68dfb.png)
Comparing this to the electrical conductance 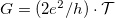 obtained from the Landauer formula:
obtained from the Landauer formula:
![\[\frac{G_Q}{G}=\mathcal{L}\cdot T;\ \ \ \mathcal{L}=\frac{\pi^2k^2}{3e^2}=2.44\times 10^{-8}\,\mathrm{W\,\Omega\,K^{-2}}\]](/images/math/f/f/3/ff3d6b12800ff710fdc4212c0c4da3ce.png)
where 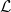 is the so-called Lorenz number. This relation shows that the electrical conductance is proportional to the thermal conductance, which is referred to as the Wiedemann-Franz law. However, it is important to note that thermal conduction may be caused by phonons, which we did not take into account in our calculations.
is the so-called Lorenz number. This relation shows that the electrical conductance is proportional to the thermal conductance, which is referred to as the Wiedemann-Franz law. However, it is important to note that thermal conduction may be caused by phonons, which we did not take into account in our calculations.
Peltier effect
Finally, let us examine the process opposite to the Seebeck effect which is called the Peltier effect. In this process at zero temperature-difference (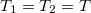 ), a finite thermal current starts to flow due to an electric current flowing through the nanowire. It is important to emphasise that the temperature-difference is zero because if it was finite, beside the thermal current from the Peltier effect another thermal current contribution would arise due to heat conduction. One can calculate the thermal current utilizing again the Sommerfeld expansion:
), a finite thermal current starts to flow due to an electric current flowing through the nanowire. It is important to emphasise that the temperature-difference is zero because if it was finite, beside the thermal current from the Peltier effect another thermal current contribution would arise due to heat conduction. One can calculate the thermal current utilizing again the Sommerfeld expansion:
![\[I_Q=\frac{2}{h} \cdot \int \mathcal{T(\varepsilon)}\cdot (\varepsilon-\mu_1)\cdot \left[f_1(\varepsilon,\mu_1,T)-f_2(\varepsilon,\mu_2,T)\right]\mathrm{d}\varepsilon\approx\frac{2}{h} \cdot \underbrace{\int_{\mu_2}^{\mu_1} \mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)(\varepsilon-\mu_1)\,\mathrm{d}\varepsilon}_{\sim (eV)^2} +\frac{2}{h}\frac{\pi^2}{6}(kT)^2\left[\overbrace{\underbrace{\left(\mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)(\varepsilon-\mu_1)\right)^\prime |_{\mu_1}}_{\mathcal{T}(\mu_1)}- \underbrace{\left(\mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)(\varepsilon-\mu_1)\right)^\prime|_{\mu_2}}_{\mathcal{T}^\prime (\mu_2)(\mu_2-\mu_1)+\mathcal{T}(\mu_2)}}^{2\mathcal{T}^\prime (\mu)\cdot eV}\right].\]](/images/math/6/c/9/6c9b71da34396b97bed9bf295652162a.png)
The first term in the Sommerfeld expansion gives a second-order contribution in the voltage, thus one can neglect it. If we reorder the remaining terms, the result for the thermal current:
![\[I_Q\approx \frac{2e}{h}\frac{\pi^2 k^2 T^2}{3}\cdot \frac{\partial \mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)}{\partial \varepsilon}\bigg|_\mu \cdot V.\]](/images/math/0/6/6/06600d8c1e78090e7cc08bc7a405a1a1.png)
The Peltier coefficient is defined as the ratio of the thermal current and the electric current 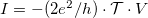 :
:
![\[\frac{I_Q}{I}\bigg|_{T_1=T_2}\approx -\frac{\pi^2 k^2 T^2}{3e}\cdot \frac{1}{\mathcal{T}}\frac{\partial \mathcal{T}(\varepsilon)}{\partial \varepsilon}\bigg|_\mu =\Pi=T\cdot S.\]](/images/math/c/7/e/c7ef529f959bf50fca1ef364b8d09e74.png)
Comparing this result with the Seebeck coefficient we get: 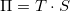 which is referred to as the Kelvin relation.
which is referred to as the Kelvin relation.